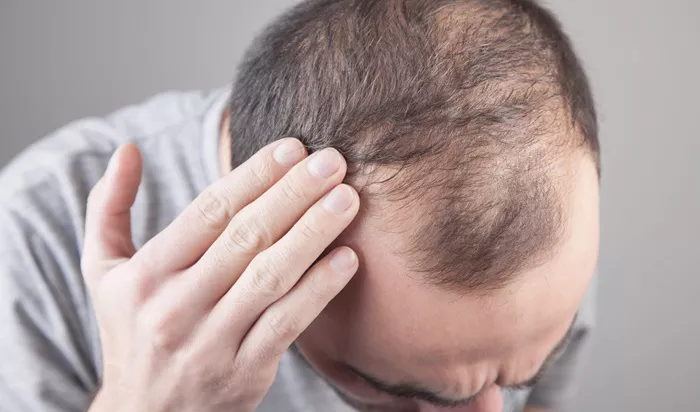
Male pattern baldness, medically termed as androgenic alopecia, is a prevalent condition affecting a significant portion of the male population worldwide. Recognizing the early signs and symptoms of male pattern baldness is crucial for seeking appropriate treatment and management strategies. As individuals seek information on this topic, it’s essential to provide a comprehensive guide that addresses the symptoms, stages, genetic factors, hormonal influences, age of onset, ethnic variations, treatment options, prevention strategies, and the importance of seeking professional medical advice.
Overview of Male Pattern Baldness
Male pattern baldness, or androgenic alopecia, is a common form of hair loss that typically follows a specific pattern. It is characterized by progressive thinning and shedding of hair, primarily on the scalp. This condition affects men of all ages and ethnicities, although the onset and severity may vary. Androgenic alopecia is primarily driven by genetic and hormonal factors, with the hormone dihydrotestosterone (DHT) playing a significant role in its development.
Symptoms
The early symptoms of male pattern baldness often include:
1.Hair thinning or loss on the crown: One of the most common signs is the gradual thinning of hair on the top of the scalp, resulting in a widening part or visible scalp.
2.Hair thinning or loss near the temples: Hairline recession, particularly around the temples, is another early indicator of male pattern baldness.
3.Receding hairline: Male pattern baldness typically begins with a receding hairline, forming an “M” shape as the hairline moves further back on the scalp.
These symptoms may start subtly and progress over time, eventually leading to more noticeable hair loss and balding.
Stages of Progression
The Hamilton-Norwood scale is commonly used to classify the stages of male pattern baldness. This scale ranges from stage I, representing minimal hair loss, to stage VII, indicating extensive balding across the scalp. Understanding the progression of male pattern baldness can help individuals assess their current stage and anticipate future hair loss patterns.
Genetic Factors
Genetics play a significant role in determining an individual’s susceptibility to male pattern baldness. Family history is often a strong indicator, with those who have close relatives experiencing baldness at a young age being more likely to develop the condition themselves. Several genetic factors contribute to the onset and progression of male pattern baldness, making it essential to consider family history when assessing one’s risk.
Hormonal Influences
Hormonal imbalances, particularly elevated levels of dihydrotestosterone (DHT), contribute to the development of male pattern baldness. DHT is a byproduct of testosterone metabolism and is known to shrink hair follicles, leading to shorter and finer hair growth. While testosterone is a crucial hormone in male development, excessive levels of DHT can negatively impact hair follicles, resulting in progressive hair loss.
Age of Onset
Male pattern baldness can manifest at various ages, with symptoms often appearing as early as the late teens to early twenties. However, the onset and progression of the condition may vary among individuals, influenced by genetic predisposition, hormonal factors, and lifestyle choices. Early recognition of symptoms and proactive management can help slow down the progression of male pattern baldness and preserve hair health.
Ethnic Variations
Male pattern baldness affects individuals from different ethnic backgrounds differently. While it is more commonly observed in individuals of European descent, it can also occur in individuals of Asian, African, and Hispanic descent. Ethnic variations in hair density, texture, and growth patterns may influence the presentation and progression of male pattern baldness in different populations.
Treatment Options
Several treatment options are available for managing male pattern baldness and promoting hair regrowth. These include:
1.Medications: FDA-approved medications such as minoxidil (Rogaine) and finasteride (Propecia) are commonly prescribed to treat male pattern baldness. Minoxidil is a topical solution that helps stimulate hair growth, while finasteride is an oral medication that blocks the conversion of testosterone to DHT.
2.Hair transplants: Surgical procedures such as follicular unit transplantation (FUT) and follicular unit extraction (FUE) involve transplanting hair follicles from donor areas to balding or thinning areas of the scalp, providing long-term hair restoration.
3.Styling techniques: Hairstyling techniques, such as camouflage products, hair fibers, and scalp micropigmentation, can help conceal thinning areas and create the illusion of fuller hair.
Prevention and Management
While male pattern baldness cannot always be prevented, certain lifestyle modifications and management strategies can help slow down its progression and maintain overall hair health. These include:
1.Maintaining a healthy diet: Consuming a balanced diet rich in vitamins, minerals, and essential nutrients can promote hair growth and minimize hair loss.
2.Avoiding harsh styling practices: Limiting the use of heat styling tools, chemical treatments, and tight hairstyles can reduce damage to hair follicles and prevent further hair loss.
3.Managing stress: Chronic stress can contribute to hormonal imbalances and exacerbate hair loss. Practicing stress-reduction techniques such as meditation, yoga, and deep breathing exercises can promote overall well-being and hair health.
When to See a Doctor
It’s essential to consult a healthcare professional if you notice any significant changes in your hair density, pattern, or texture. A dermatologist or hair specialist can provide a thorough evaluation, diagnose the underlying cause of hair loss, and recommend appropriate treatment options. Early intervention is key to effectively managing male pattern baldness and preserving hair quality.
In conclusion, male pattern baldness is a common condition that can significantly impact self-esteem and quality of life. By recognizing the early symptoms, understanding the underlying factors, and exploring available treatment options, individuals can take proactive steps to address male pattern baldness and maintain healthy hair. Seeking professional medical advice and adopting preventive measures are essential components of managing this condition effectively. Remember, you’re not alone in this journey, and support is available to help you navigate the challenges of male pattern baldness with confidence and resilience.
you may be interested